Learn how PSU watts affect your GPU’s effective performance and longest lifespan. We explain how you can calculate the wattage requirement for your PSU and why the power draw of modern GPUs is so important in 2025.
What is power supply wattage?
PSU wattage is the maximum power it produces and supplies to your PC components at full load. In general, a properly selected PSU delivers exactly as much power as all of your PC components need to work efficiently and without failure. When it comes to selecting PC components with the intention of ensuring stable performance under maximum load, knowing how much wattage you need altogether is key.
When calculating how much wattage is needed to power the entire system, you start by adding up the power usage of each component to figure out what power supply you will need. Adding up the power rating of the processor, the graphics card (GPU), the RAM, and storage devices will give you the total wattage required to power your PC. A good power supply will ensure that all these components perform their tasks and operate without overheating or breaking down at all times.
Seasonic, in general, also recommends adding about 20 % to 30 % to the initially calculated total wattage as a buffer to make sure that the PC’s performance during peak loads remains stable and that there is enough overhead for future upgrades or potential overclocking.
In summary, the PSU power rating should have enough reserve capacity to provide your computer with sufficient energy for a long time. For safe and efficient operation, choose a PSU with the calculated power plus a reserve and aim for a high efficiency certification (80 PLUS® Platinum or Titanium).
Why is PSU wattage important when installing a new GPU?
Here are a few key reasons to keep in mind in terms of PSU wattage when installing a new GPU.
- The GPU’s high power consumption
Modern top-of-the-line video cards can consume up to 350–600 W of power or more. For example, the RTX 3090 can reach around 450 watts during peaks, whereas the RTX 5090 can reach up to 575 W and sometimes even more. Knowing the power requirements of a specific GPU is very crucial, and you can find out more about this from the manufacturer’s documentation.
- Transient spikes
Under high load situations (like intensive gaming, rendering, etc.), the GPU can suddenly increase its consumption above the nominal TDP (Thermal Design Power). For example, in the case of the RTX 5090, this value can spike from 575 W to 625 W for tens of milliseconds (Source: Igor’s Lab). It is crucial, therefore, that the PSU must be able to handle such loads without a voltage drop.
- Power reserve
It’s usually recommended to pick up a PSU with a reserve of 20 % to 30 % extra power, so that it can operate at around 50 % to 75 % of its rated output. This ensures high PC performance, lower component heating, lower fan noise, and it also slows down wear and tear on all the computer parts.
- System stability and protection
A power supply with insufficient power can cause system instability, which manifests itself in reboots, shutdowns, performance degradation, overheating, or even component damage. That is why it’s recommended to calculate with an extra 20 % to 30 % extra headroom above the rated power of the PSU when selecting the proper power supply for a PC.
- Power connector compatibility
The most recent graphics cards use 16-pin (12V-2×6) connectors, but older power supplies might not have the right connectors supplied in the packaging or may need extra adapters that can be incompatible or even unsafe. Therefore, Seasonic advises checking the power supply and component compatibility very carefully before buying, to ensure that everything works properly.
What is the typical power draw of modern GPUs in 2025?
The flagship NVIDIA RTX 5090 and RTX 5080 GPU models have the highest consumer demand because they can handle even the heaviest tasks, and with the support of a good power supply, they do that without interruptions.
The power needs of the different GPUs vary; the RTX 5090’s power consumption can sometimes peak at 700 W or more, while the RTX 5080 model, on the other hand, consumes only about 360 W on average. The mid-range RTX 5070 and RX 7800 XT models consume less energy than the top models, with their TDP between 250 W and 360 W. Budget GPUs like RTX 4060 and RX 7600 usually consume up to about 200 W to 250 W.
There are some approximate power draw consumption values in this table:
| GPU Tier | GPU Model | TGP (Watt) | Peak loads |
|---|---|---|---|
| Budget | RX 7600, RTX 4060 | ~160–190 | ~200–250 W |
| Mid-range | RTX 5070 / 7800 XT | ~250–360 | Up to ~400 W |
| Flagship | RTX 5080 | ~360 | ~400–450 W |
| Flagship | RTX 5090 | ~575 | > 700 W |
Knowing these values before selecting a power supply is very useful, as out of all the PC components, the GPU is the one that draws the most power. There can be more considerations to look for when selecting the best PSU for a system, such as efficiency certifications (80 PLUS® Platinum or Titanium), PCIe 5.1 support, and the number of 12V-2×6 connectors for high-power GPUs.

How to calculate the total power requirements of your system?
The Seasonic wattage calculator will assist in estimating the power consumption for you. To make this indicator as accurate as possible, the calculator guides you through the process of collecting power data on all your PC components. In other words, you will need to add up the power consumption values of every single component in your PC (processor, graphics card, storage, and cooling) for accurate wattage calculation and to pick the perfect matching power supply.
The Seasonic power supply calculator will also automatically add a 20 % to 30 % power usage reserve for potential peak loads or hardware upgrades, and at the final stage, it gives you an adjusted wattage value, which will be key for choosing the right power supply with the necessary power to support your PC for a long time.
How much headroom should you leave beyond the GPU’s wattage?
Here are the core recommendations:
- Add 10 % to 20 % reserve above the calculated PSU peak consumption as an acceptable minimum standard for modern builds.
- 20 % to 30 % extra power is recommended for potentially more intensive GPU performance, future upgrades, or overclocking.
Why is it so important to go through these steps?
It is known that PSUs work most efficiently at loads between 50 % and 70 % of their rated capacity. If you are running a system too close to its maximum capacity, it lowers efficiency and generates more heat and fan noise, so the proper power rating is more than just a “nice to have” indicator.
Over time, the capacitors in the PSU generally wear down, and the actual effective power usually decreases a bit. The calculated power reserve also helps to maintain stability over the years. Moreover, a PSU with a reserve allows you to install new, more powerful GPUs/CPUs or add new storage devices without having to replace the power supply.

Is it necessary to upgrade the PSU for high-end GPUs?
It is not always necessary to upgrade the power supply when you buy a new GPU, but if your PSU does not supply enough power to handle a new, higher-end GPU, it becomes unavoidable to upgrade the power supply as well. On the other hand, however, you might not need to upgrade your power supply if it supplies enough power (with headroom included), it is not too old (up to about 5 years old), and meets the GPU manufacturer’s power requirements.
In case you have an older or a low-budget power supply, there is a risk that even at the stated power rating, it will not be able to handle the peak loads generated by a high-performance GPU, which will lead to system crashes.
Another important point to consider is connector compatibility. New graphics cards use the 12V-2×6 (16-pin) power standard, and if the power supply cannot comply with this standard, replacing it will be necessary.
In summary, before installing a new GPU, you should carefully check if your power supply meets all the technical requirements and upgrade it if necessary to avoid future problems.

What are the risks of using an underpowered PSU?
You should always pick a PSU that has enough power to easily support the safe operation of all your PC components. The very first step you need to take to make sure you select the proper power apply for your system is to use the Seasonic wattage calculator. The calculator provides some recommendations that help you choose the appropriate PSU for your PC that will be able to support your PC’s live and stable operations under different loads, including peak times.
Instability is the first thing you will notice with an underpowered PSU. If you do not have a strong enough power supply, sudden shutdowns, reboots, or complete failures can occur under heavy load situations. When the PC goes into peak mode (gaming, rendering), and there is not enough power, the system will shut down, and you might lose progress or valuable data.
With an underpowered PSU, there can be some issues related to performance. Due to unstable voltages, components will not work properly, resulting in freezes, FPS drops, and reduced performance. Unexpected shutdowns can also potentially damage operating system files.
Another risk is damage to your PC components. An underpowered PSU can cause system instability, crashes, or unexpected shutdowns. In severe cases, especially with low-quality power supplies, it may lead to electrical overloads that can damage the PSU itself and potentially harm other components like the motherboard, CPU, GPU, or storage devices.
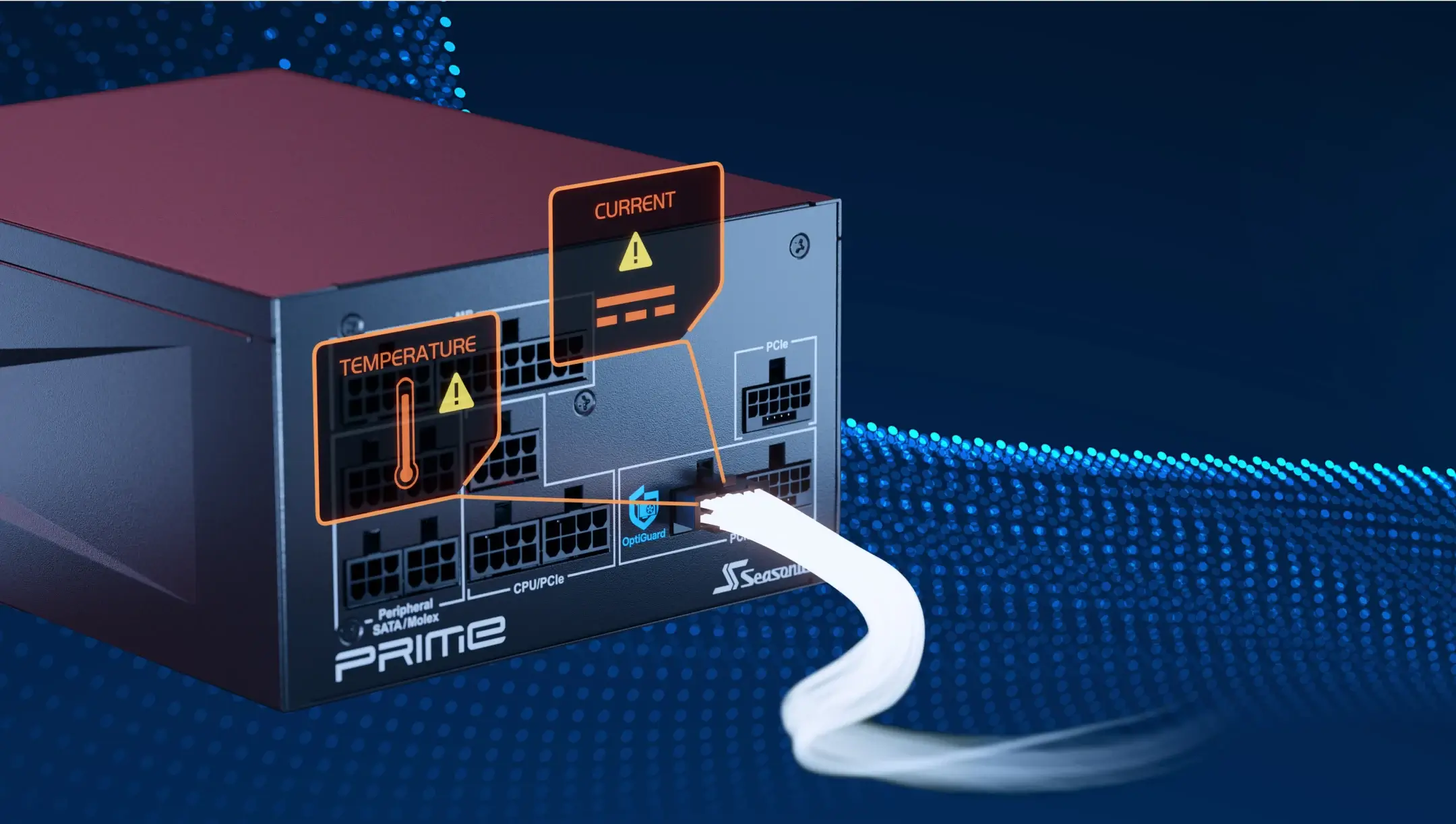
What wattage ratings do GPU manufacturers recommend for power supplies?
Graphics card manufacturers like NVIDIA and AMD also have their own power supply recommendations. According to these companies, it is better to choose PSUs with a power rating of 650 W to 1000 W for mid-range and high-end graphics cards.
When selecting a power supply to match your GPU, it is also important to consider not just the video card’s power consumption, but that of other components as well. After all, the PSU has to be able to provide the power necessary to handle the stable operation of each and every PC component. Once you know the GPU’s power consumption, and you add the other components’ power needs, you get a final figure that will help you choose your highly productive PSU.
Which other components significantly affect overall power consumption?
In addition to the graphics card, other PC components also consume energy. To get an idea of how much, here are more details:
CPU: Its energy consumption can range from 35 W to over 200 W. CPU power consumption depends on the model, core number, and clock speed. Therefore, you have to know the exact make and model of the CPU to add the correct value to the total system power consumption.
Motherboard: It consumes around 25 W to 80 W of power; some top models can even run on up to 100 W of power, depending on the chipset, or features such as built-in Wi‑Fi, audio, VRM, etc.
Random access memory (RAM): Each DDR3–DDR5 module consumes about 2 W to 5 W of power, with faster or overclocked modules consuming slightly more.
Storage (SSD, HDD): SSD requires about 2 W to 5 W, while HDD consumes 6 W to 12 W of power at peak, potentially reaching 15 W during intensive operation.
Cooling system and additional components: Each case fan uses 2 W to 6 W, water cooling pumps and RGB lighting use 5 W to 20 W, depending on their complexity.
A combination of the components we have described can add 50 W to 150 W to the system’s total power consumption. Therefore, do not forget to consider these data when picking the right PSU to ensure reliability during peak loads and some necessary power reserve.
How do 80 PLUS® certified modular power supplies help ensure power and stability?
The 80 PLUS® certification means that at least 80 % of the electricity consumed is converted into useful energy. The valuations are given at loads of 20 %, 50 %, and 100 % loads. The most efficient certification levels, valued and chosen by computer enthusiasts, are Gold, Platinum, and Titanium. Gold starts at about 90 % efficiency at 50 % load, and Titanium efficiency goes as high as 96 %.
Modular power supplies let you connect only the cables that you need for your PC components to work efficiently. Fully modular PSUs have lots of advantages. First, they reduce clutter inside the case and improve system ventilation and cooling. Second, they contribute to less heat generation and increased power stability. It is important to mention, however, that the usage of proper cables matching a specific PSU model can further protect the system from damage caused by incorrect connections.
Advantages of 80 PLUS® certified modular power supplies for stability and reliability:
- Lower heat dissipation means less energy is lost as heat. This results in optimal case temperature and reduced fan noise.
- Higher voltage quality and lower ripple. Certified PSUs often use higher quality components, which ensure more stable output voltages. They also minimize voltage fluctuations within a ± 1% range and support overclocking without performance drops.
- Greater reliability and durability. 80 PLUS® certified PSUs (especially Platinum and Titanium) usually have better design, higher quality components, and less likelihood of failure. A good example of this would be Seasonic power supplies from the PRIME and VERTEX lines. These models come with a 12-year warranty from Seasonic, and many real user reviews rave about the high efficiency and quality of the power supply itself.
Conclusion
Choosing the PSU that aligns with your GPU power needs is a complex process where you need to add together the power consumption of all the PC components power consumption, and take into account some extra power for upgrades or peak load situations.
Your PC’s lifespan and performance depend on choosing the right power supply with enough power for all components. We recommend choosing 80 PLUS® certified PSUs (Platinum/Titanium) with PCIe 5.1 and one or two 12V-2×6 connectors for high-power GPUs.


























